Ever stared at an Excel formula and seen a strange symbol like a $ dollar sign, an & ampersand, or a ^ caret and wondered what it does? You’re not alone. This guide is your definitive cheat sheet.
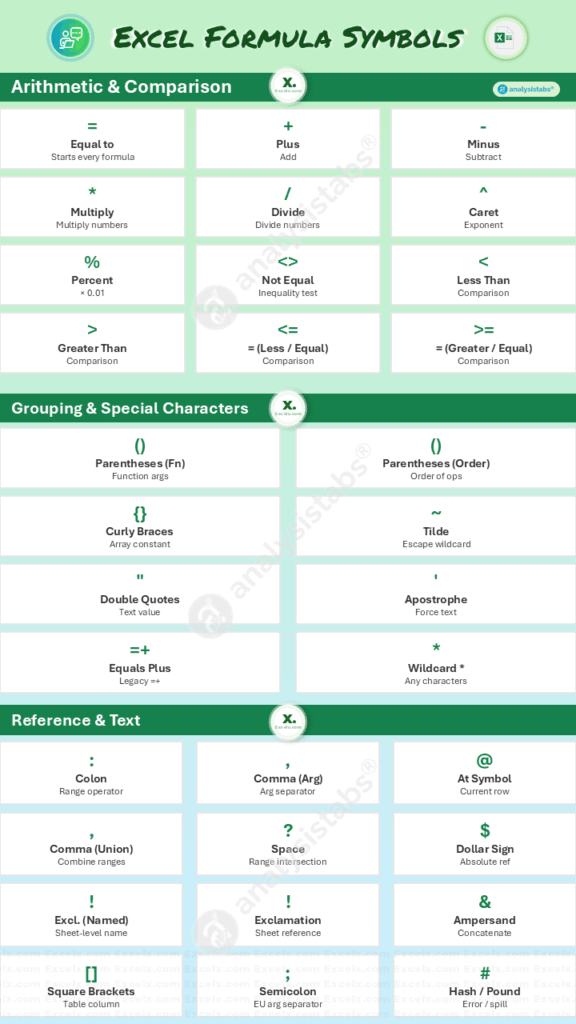
Quick Reference Table: All Excel Symbols
This table provides a quick overview of the most common symbols used in Excel formulas. Find the symbol you’re looking for to get a brief description and an example.
| Symbol | Name | Quick Description & Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Equal to | Starts every formula. =A1+B1 |
| () | Parentheses (Functions) | Encloses the arguments of a function. =SUM(A1:A5) |
| () | Parentheses (Order) | Groups expressions to control the order of operations. =(5+2)*3 |
| * | Asterisk (Wildcard) | Acts as a wildcard to represent any number of characters. =COUNTIF(A1:A5,"*apple*") |
| , | Comma (Separator) | Separates arguments in a function. =IF(A1>10, "High", "Low") |
| & | Ampersand | Joins two text strings together (concatenate). ="Pro" & "ject" |
| $ | Dollar Sign | Creates an absolute reference (locks a row/column). =$A$1 |
| ! | Exclamation (Sheet Ref) | Separates a sheet name from a cell reference. =Sheet2!A1 |
| [] | Square Brackets | Refers to a column in an Excel Table. =SUM(MyTable[Sales]) |
| {} | Curly Braces | Creates an array constant or denotes an array formula. ={1,2,3} |
| : | Colon | Creates a reference to a continuous range of cells. =SUM(A1:A10) |
| , | Comma (Union) | Combines multiple ranges into one reference. =SUM(A1:A5,C1:C5) |
| (space) | Space (Intersection) | Finds the common cells between two ranges. =SUM(Range1 Range2) |
| ! | Exclamation (Named Range) | Used in named ranges to define sheet-level scope. |
| + | Plus | Arithmetic operator for addition. =5+2 |
| – | Minus | Arithmetic operator for subtraction. =5-2 |
| * | Asterisk (Math) | Arithmetic operator for multiplication. =5*2 |
| / | Forward Slash | Arithmetic operator for division. =10/2 |
| ^ | Caret | Raises a number to a power (exponent). =5^2 |
| # | Hash / Pound | Prefixes all error names (e.g., #N/A) and spill ranges (#SPILL!). |
| @ | At Symbol | Refers to the current row in a Table or indicates implicit intersection. =[@Sales] |
| % | Percent Sign | Divides by 100. 50% is treated as 0.5. |
| <> | Not Equal To | Compares if two values are not equal. =IF(A1<>B1, "Different", "Same") |
| < | Less Than | Compares if one value is less than another. =IF(A1<100, "Low", "High") |
| > | Greater Than | Compares if one value is greater than another. =IF(A1>100, "High", "Low") |
| <= | Less Than or Equal To | Compares if a value is less than or equal to another. =IF(A1<=100, "Pass", "Fail") |
| >= | Greater Than or Equal To | Compares if a value is greater than or equal to another. =IF(A1>=100, "Pass", "Fail") |
| ; | Semicolon | Used as an argument separator in some European regional settings. =SUM(A1;A2) |
| ~ | Tilde | Acts as an escape character for wildcards like * or ?. |
| \ | Backslash | Used in file paths when referencing external workbooks. |
| =+ | Equals Plus | Historical notation; functionally the same as =. =+A1+B1 |
| “ | Double Quotes | Encloses a text string. =IF(A1="Complete", "Done", "Pending") |
| ‘ | Apostrophe | When used at the start of a cell, forces the content to be treated as text. |
Detailed Breakdown of Excel Operators
For a deeper understanding, let’s explore how these symbols work in different contexts.
1. Arithmetic Operators
These are the symbols used for performing mathematical calculations.
+(Addition): Adds numbers together.-(Subtraction): Subtracts the second number from the first.*(Multiplication): Multiplies numbers./(Division): Divides the first number by the second.^(Exponentiation): Raises a number to a power.%(Percentage): Divides a number by 100.
2. Comparison (Logical) Operators
These operators are used to compare two values and always result in either TRUE or FALSE.
=(Equal to): Checks if two values are equal.<>(Not equal to): Checks if two values are not equal.>(Greater than): Checks if the first value is greater than the second.<(Less than): Checks if the first value is less than the second.>=(Greater than or equal to): Checks if the first value is greater than or equal to the second.<=(Less than or equal to): Checks if the first value is less than or equal to the second.
3. Text Concatenation Operator
&(Ampersand): This joins two or more text strings into a single string.
4. Reference Operators
These symbols are used to work with cell references and ranges.
:(Colon): The range operator. It creates a reference to all cells between two points.,(Comma): The union operator. It combines multiple references into a single reference.!(Exclamation Mark): Separates a sheet name from a cell reference.
Understanding Display & Error Symbols
Sometimes, what you see in a cell isn’t an operator, but an indicator from Excel that something is wrong.
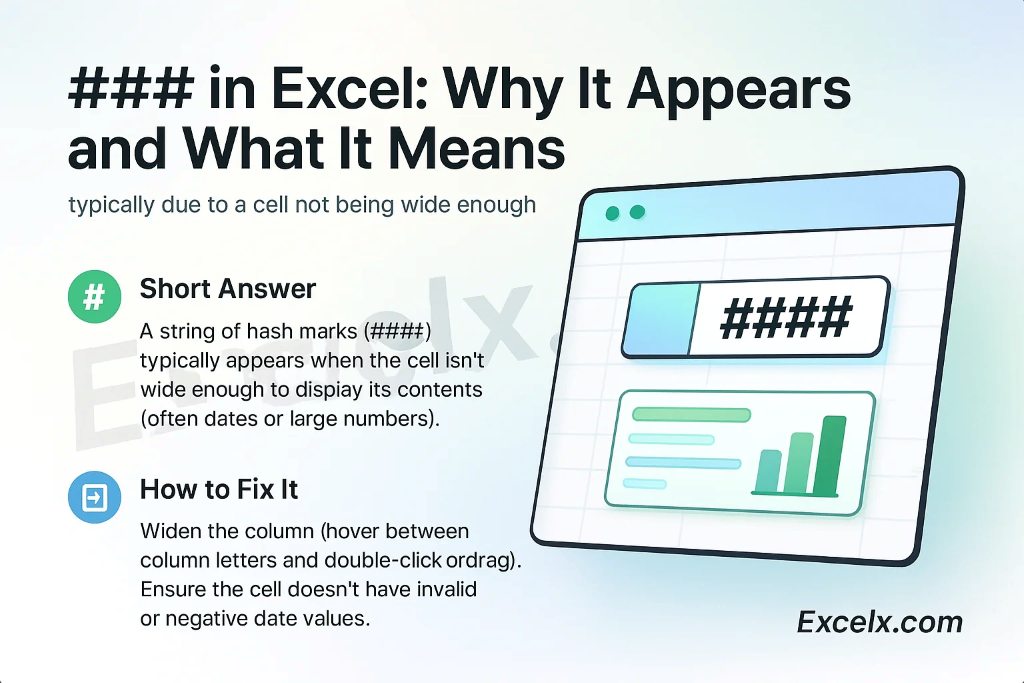
#### in Excel: Why It Appears and What It Means
If you see a cell filled with hash marks (#######), it is not a formula error. It is almost always a formatting issue.
- What it means: The column is too narrow to display the entire number or date in the cell. Excel displays
####to avoid showing an incomplete, and therefore incorrect, value. - How to fix it: Double-click the right border of the column header to automatically resize the column to fit the content.
The # Family in Excel: Formula Errors
When your formula has a logical problem, Excel returns an error code that always begins with a hash (#) symbol. Understanding these codes is the first step to fixing your formula.
#N/A: “Not Available.” The formula cannot find the value it was asked to look for.#VALUE!: The formula has the wrong type of argument (e.g., trying to add text to a number).#REF!: “Invalid Reference.” The formula refers to a cell that was deleted.#DIV/0!: “Division by Zero.” The formula is attempting to divide by zero.#NAME?: Excel doesn’t recognize the name of the function or named range.#NULL!: The two ranges in your formula do not intersect.#SPILL!: A dynamic array formula’s results are blocked by other data.
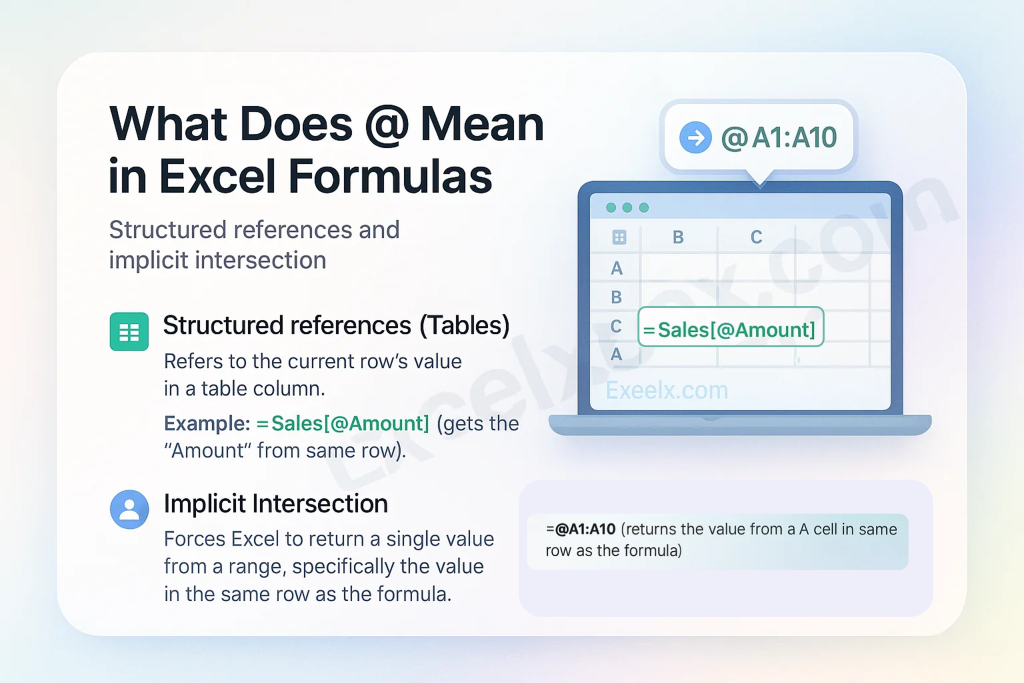
The @ Symbol: Implicit Intersection & Table References
The @ (At Symbol) has become more visible in modern Excel with the introduction of dynamic arrays. It has two primary functions.
1. Implicit Intersection
The @ symbol is used to explicitly tell Excel you want to force a formula that could return multiple values (an array) to return only a single value from the same row.
2. Structured References in Excel Tables
This is the most common place you will see the @ symbol. When you are working inside an Excel Table, the @ is a shortcut that means “this row.”
- Example:
=[@Quantity]*[@Price] - Result: This formula multiplies the quantity and price from the same row within the table.
Download the Excel Symbols Cheat Sheet
To keep a handy reference, download our free PDF cheat sheet that covers all the symbols discussed in this guide.
what is the symbol of average in excel?
You can use AVERAGE()Function to calculate Average in Excel. If you wants to show the Average Statistical Symbol (x-bar), You can insert from symbols. F7C2 is the Unicode Hexa character for X-bar symbol. Make sure that you have set the Symbol Font :MS Reference Sans Serif.
I have a workbook, where the original author used an @ sign in front of a function call in a formula. I can find no reference as to what the @ does, or how it is used. Any one know??
VBA Example: ActiveSheet.Range(“L2”).Formula = “=@CATEGORY($E2,LFC_AreaLU)”
Note: Category is a User Defined Function in the workbook.
@ is an Implicit Intersection Operator:
Implicit intersection operator: @
I have this formula, do you know what the al means in the formula ?
IF(E4=””,””,VLOOKUP(C4,al,5,0)*E4), can
It could be a defined Name or a name of the Table (List Object)
The double quotes in the formula you provided are used to represent an empty string
What does a white cross symbol mean?
When you hover on any Cell, Excel shows White Cross Symbol to indicate that you can select the specific Cell/Cells.
£
=AND($16>0,K$4 = $E6 – WEEKDAY($E6, 2)+1)
I used this formula and it was invalid.
When I use the $16 in any formula it gets rejected?
any thoughts?
You can not use $16, you should refer any range with Column Names and Row Numbers, like: $A16, $B$5 and $I6. Here $ symbol used for absolute reference of any range.