Ever wondered what Microsoft Excel is actually for? You’ve probably seen the iconic green logo or the grid of cells, but Excel is much more than just a digital spreadsheet. It’s one of the most powerful and essential software tools included in the Microsoft 365 suite, used by professionals in every industry across the globe.
In simple terms, Excel is a spreadsheet program that allows you to store, organize, analyze, and visualize data. From managing a simple project budget to creating complex financial models, Excel provides the tools to turn raw data into meaningful insights.
This guide will walk you through everything a beginner needs to know, from the basic components to the powerful features that make it an indispensable skill in 2025.
Key Takeaways
- What is it? Excel is a spreadsheet application for organizing, calculating, and analyzing data in rows and columns.
- Who uses it? Everyone from students and project managers to financial analysts and scientists.
- What can it do? Perform calculations, create charts and graphs, manage budgets, track projects, and automate repetitive tasks.
- Why is it important? Excel proficiency is a critical skill for a vast number of jobs and is essential for data-driven decision-making.
What is Excel Used For? (Real-World Examples)
While Excel can be used for almost anything involving numbers and lists, its power shines in a few key areas. Here are some of the most common uses for Excel in the professional world.
1. Data Analysis & Interpretation
This is Excel’s core strength. You can take thousands of rows of raw data and quickly make sense of it.
- Sorting and Filtering: Instantly organize data to find what you need.
- PivotTables: Summarize large datasets to identify trends and patterns without writing a single formula.
- Formulas & Functions: Perform complex calculations to find totals, averages, and much more.
2. Data Visualization
Data is more impactful when it’s visual. Excel allows you to transform your numbers into professional charts and graphs to tell a compelling story.
- Charts: Create bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and waterfall charts to visualize trends.
- Conditional Formatting: Automatically apply colors, icons, and data bars to your cells to highlight important information, like tasks that are overdue or sales figures that are below target.
3. Budgeting and Financial Management
Excel is the go-to tool for financial professionals and for managing personal finances.
- Creating Budgets: Build detailed budgets for your department, a project, or your household.
- Financial Modeling: Create complex models to forecast revenue, analyze investments, and value a company.
- Expense Tracking: Keep a running log of all your expenses to see where your money is going.
4. Project Management
Project managers rely on Excel to keep their projects on track and on budget.
- Gantt Charts & Timelines: Create visual project schedules to track tasks, durations, and dependencies.
- Task Lists: Manage and prioritize tasks, assign them to team members, and track their status.
- Resource Planning: Allocate resources, track availability, and ensure your team isn’t overloaded.
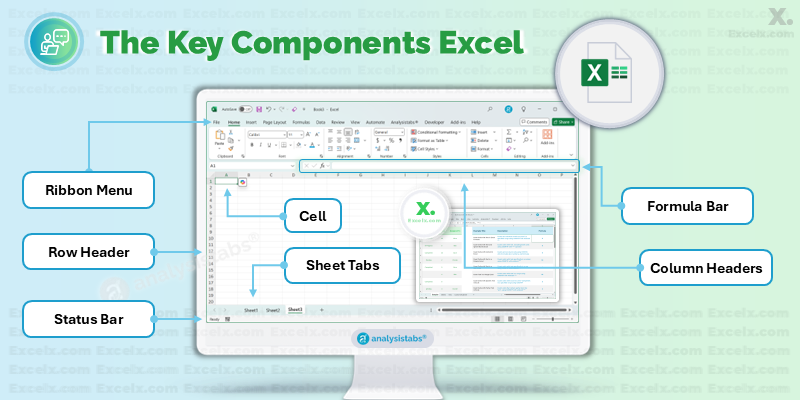
The Key Components of Excel: A Quick Tour
When you open Excel, you’ll see a grid of cells. Here are the key components you need to know.
- Ribbon: The top menu bar containing all of Excel’s tools, organized into tabs like “Home,” “Insert,” and “Formulas.”
- Workbook: The entire Excel file (e.g.,
MyProject.xlsx). - Worksheet (or Sheet): A single “page” or “tab” within a workbook. A workbook can have multiple worksheets.
- Cell: A single box in the grid where you enter data. Each cell has a unique address (e.g.,
A1,B2). - Row: A horizontal line of cells, numbered from 1 onwards.
- Column: A vertical line of cells, lettered from A onwards.
- Formula Bar: The bar above the grid where you can see and edit the formula or value in the selected cell.
Conclusion: Why You Should Learn Excel Today
Whether you are a student, a job seeker, or a seasoned professional, mastering Excel is one of an essential skills that can significantly boost your productivity and career prospects. Its versatility makes it an invaluable tool for anyone who works with data.
Ready to get started? The best way to learn is by doing. Explore our library of Free Excel Templates to see practical examples in action, or dive into our guide on the Top 10 Excel Formulas for Beginners.

so helpful
Thank you!