TL;DR Cheat-Sheet — Need to quickly reference the
IFCellContainslogic? Download our Excel IF Cell Contains Cheat-Sheet.pdf for instant access to quick steps, common formulas, and troubleshooting tips.
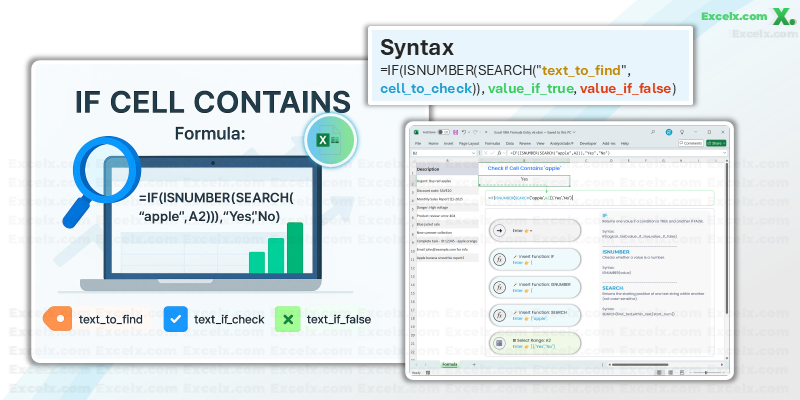
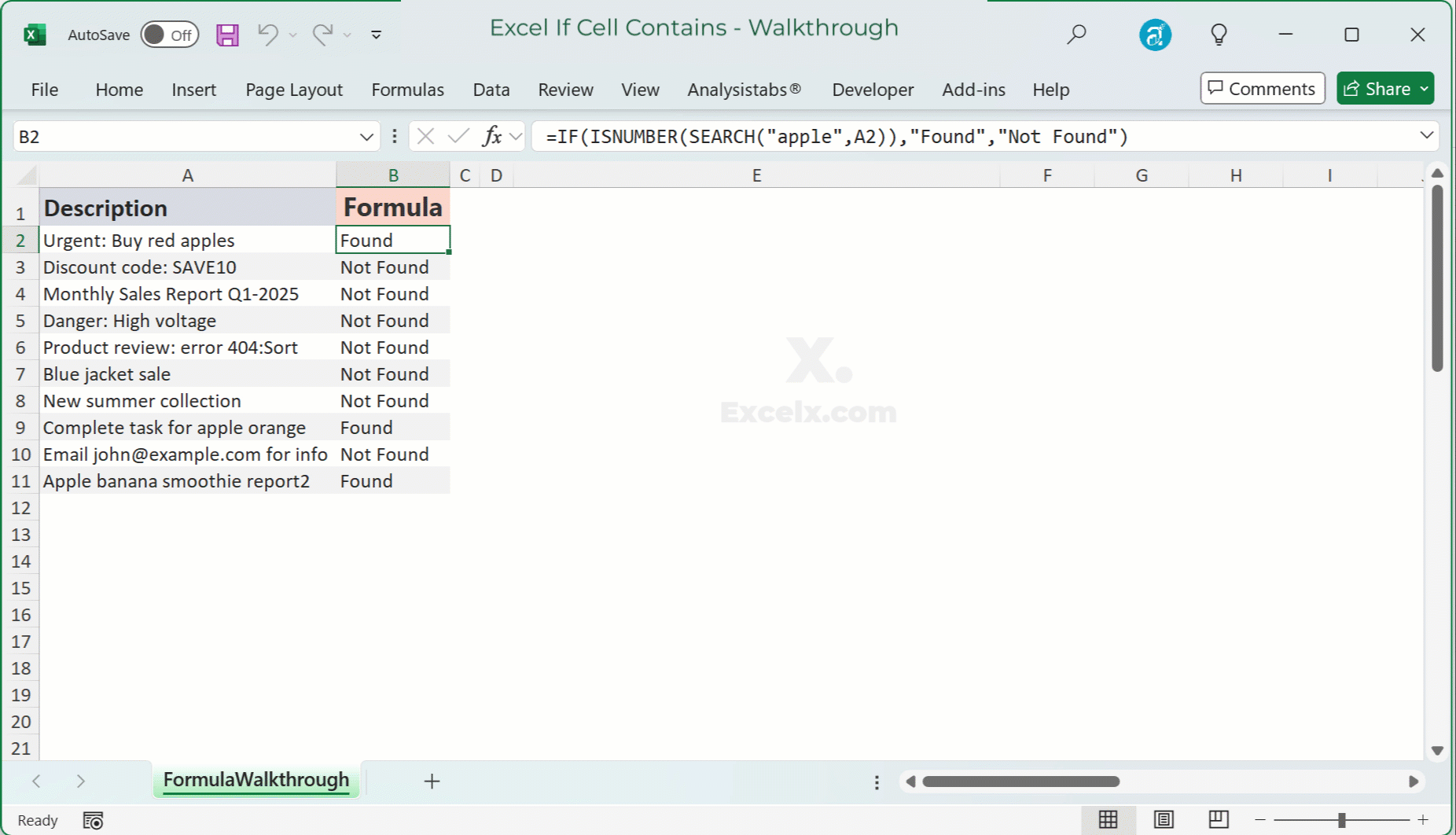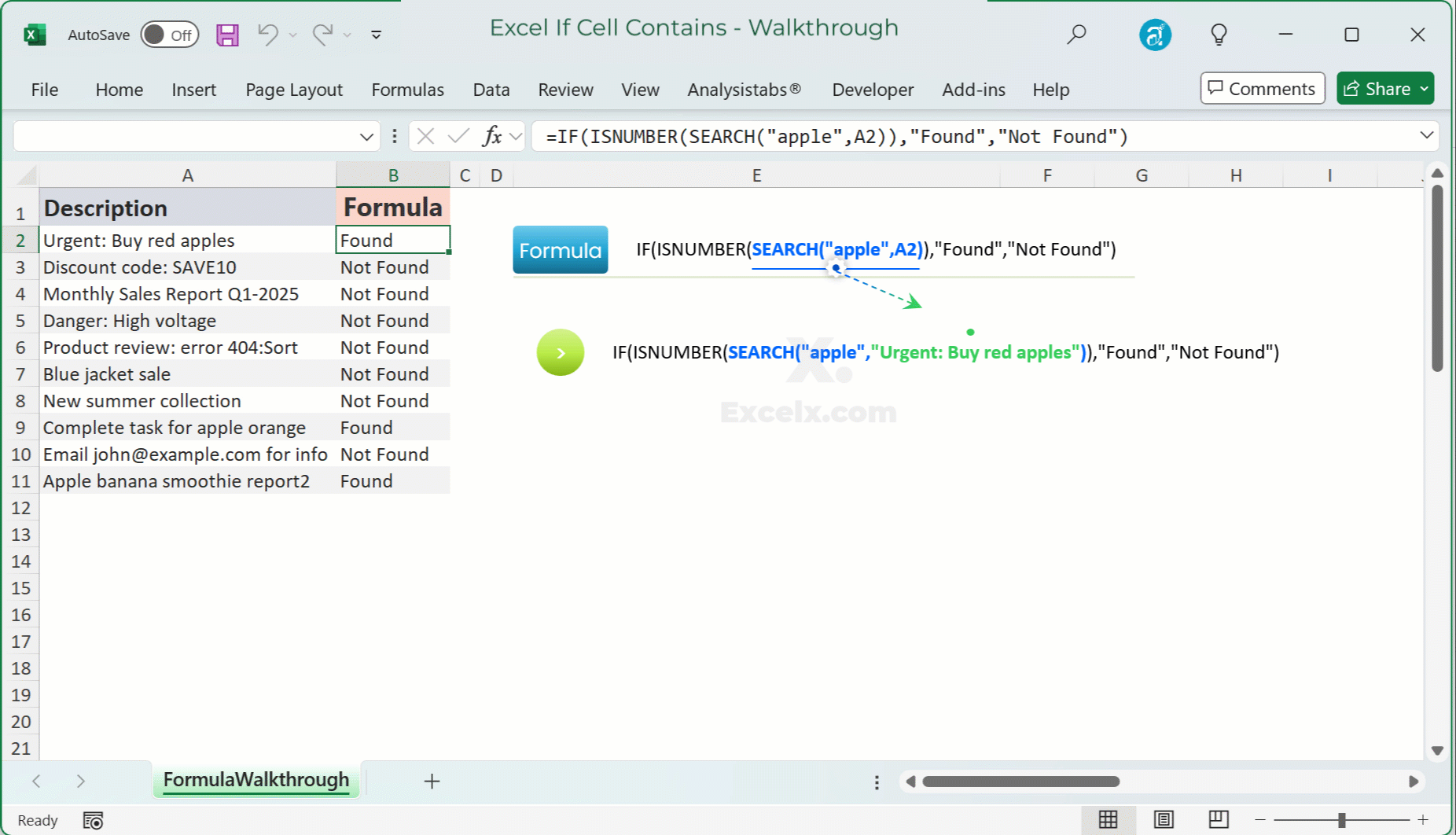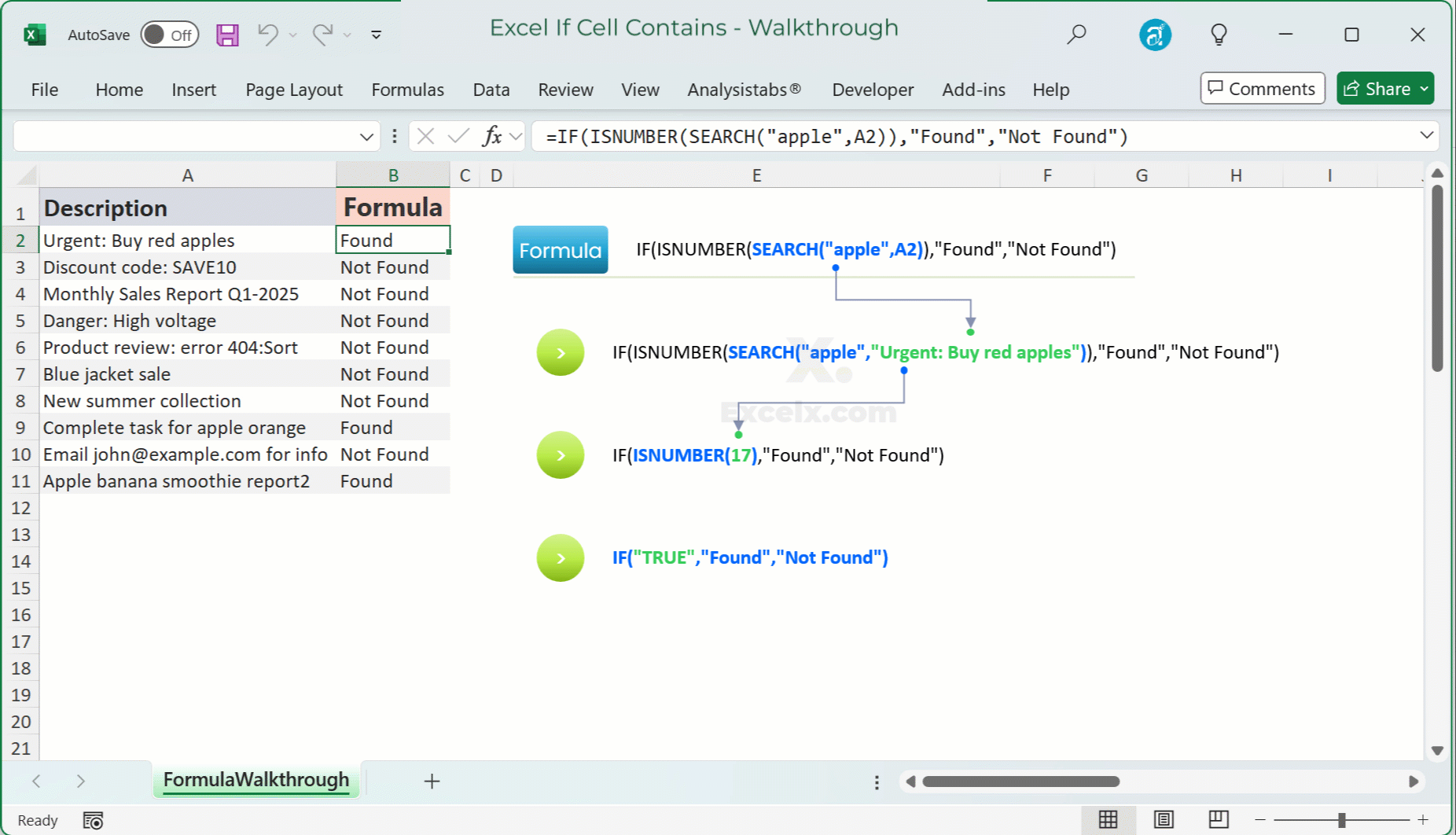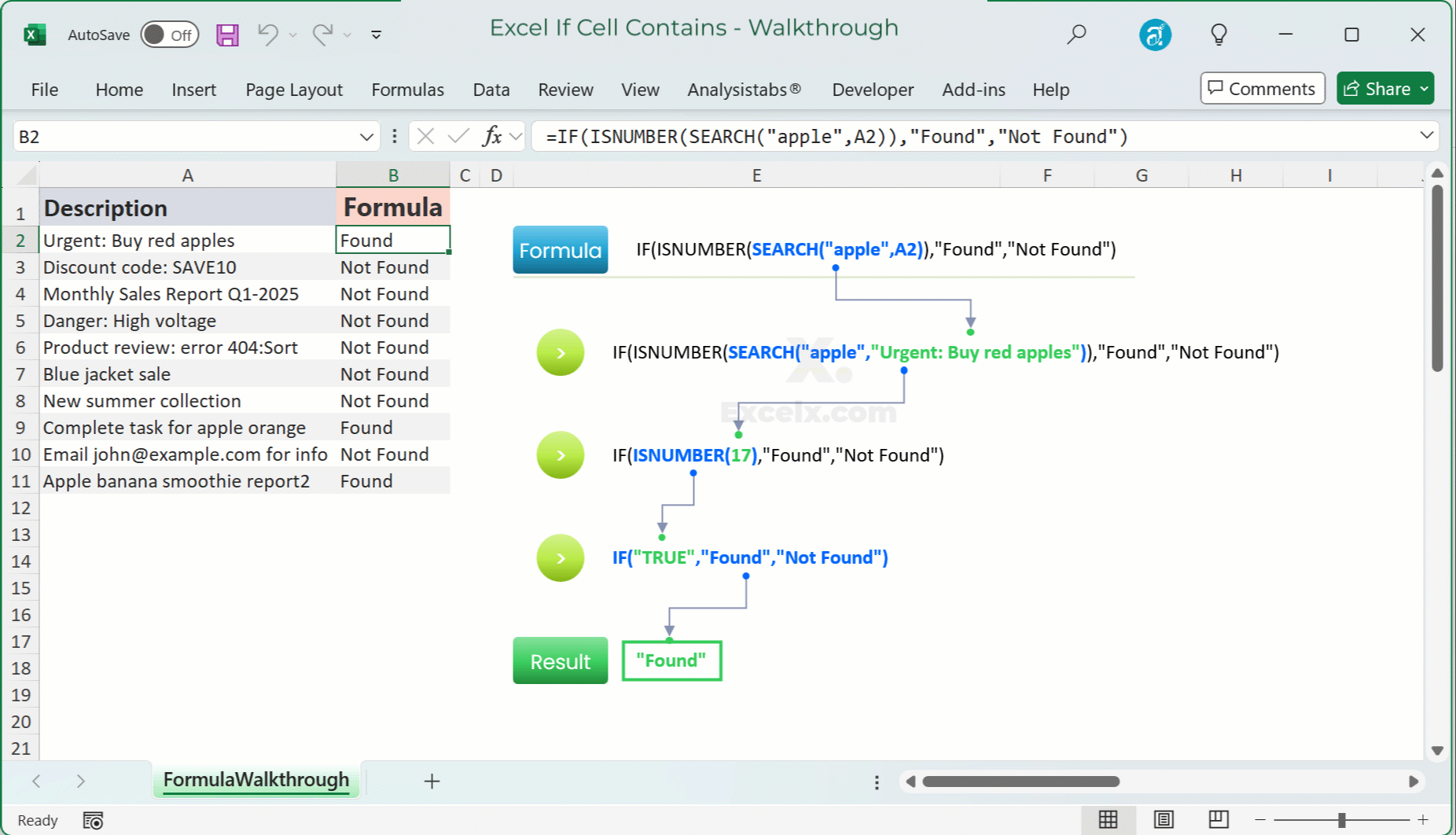
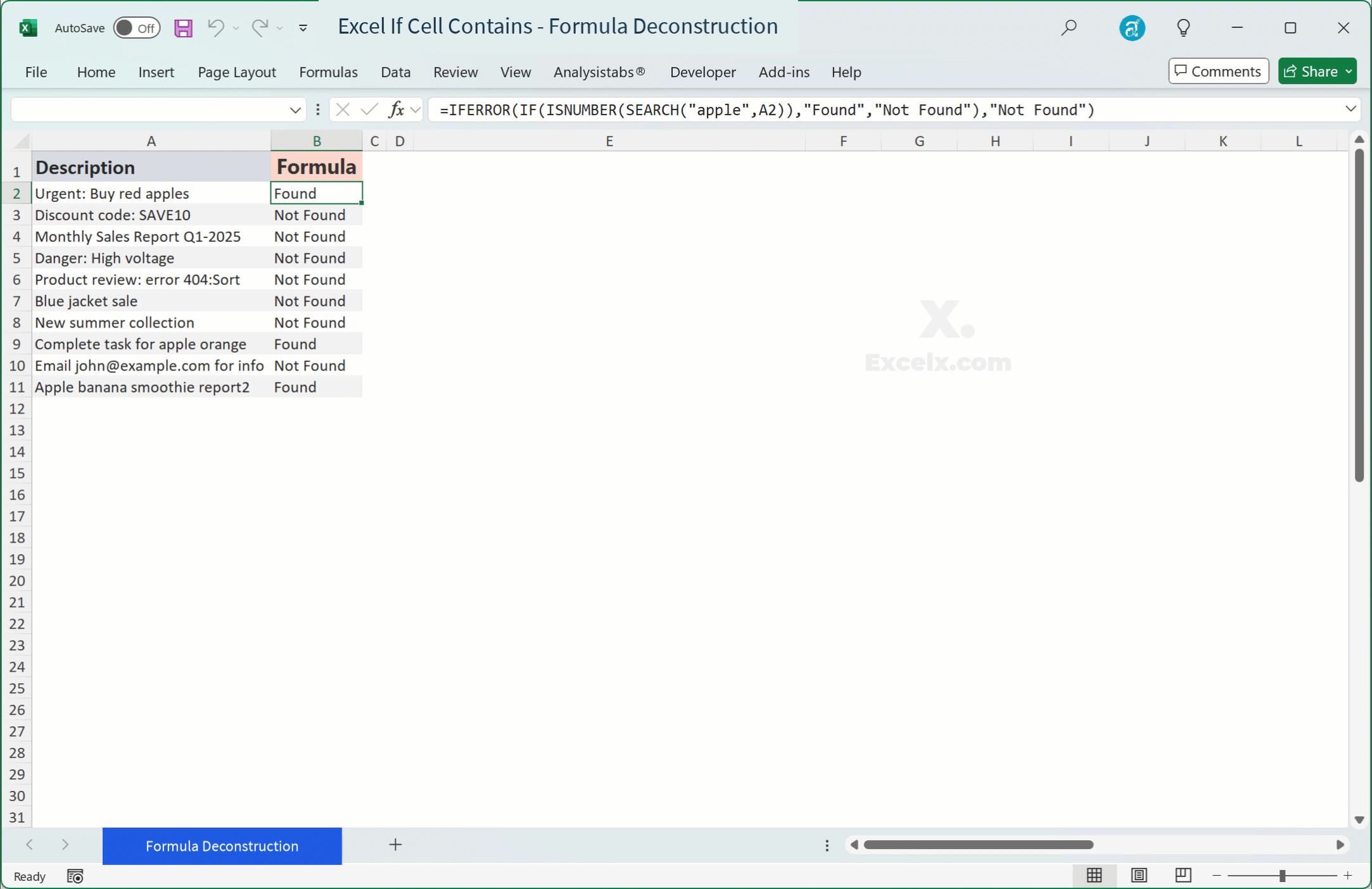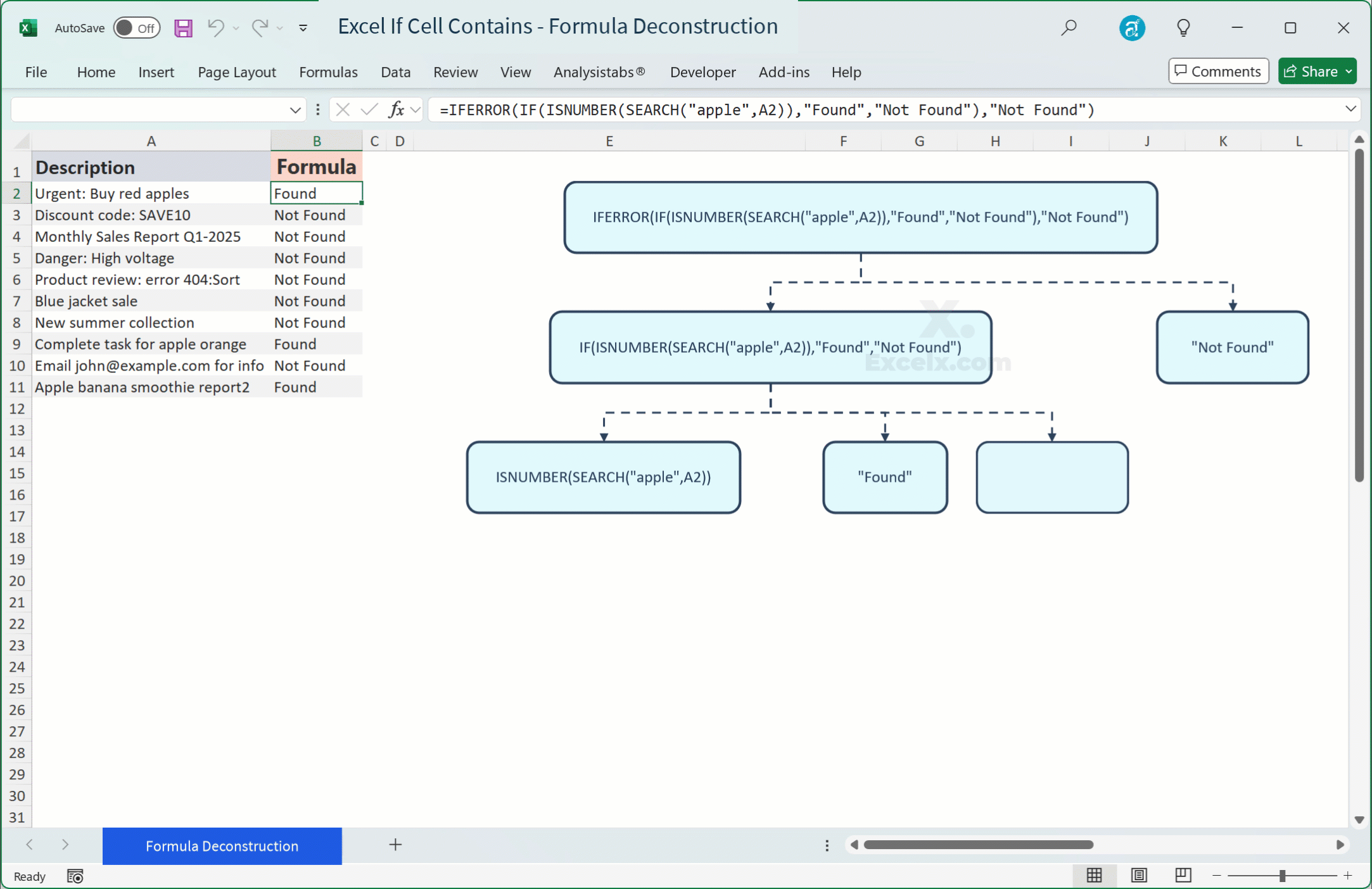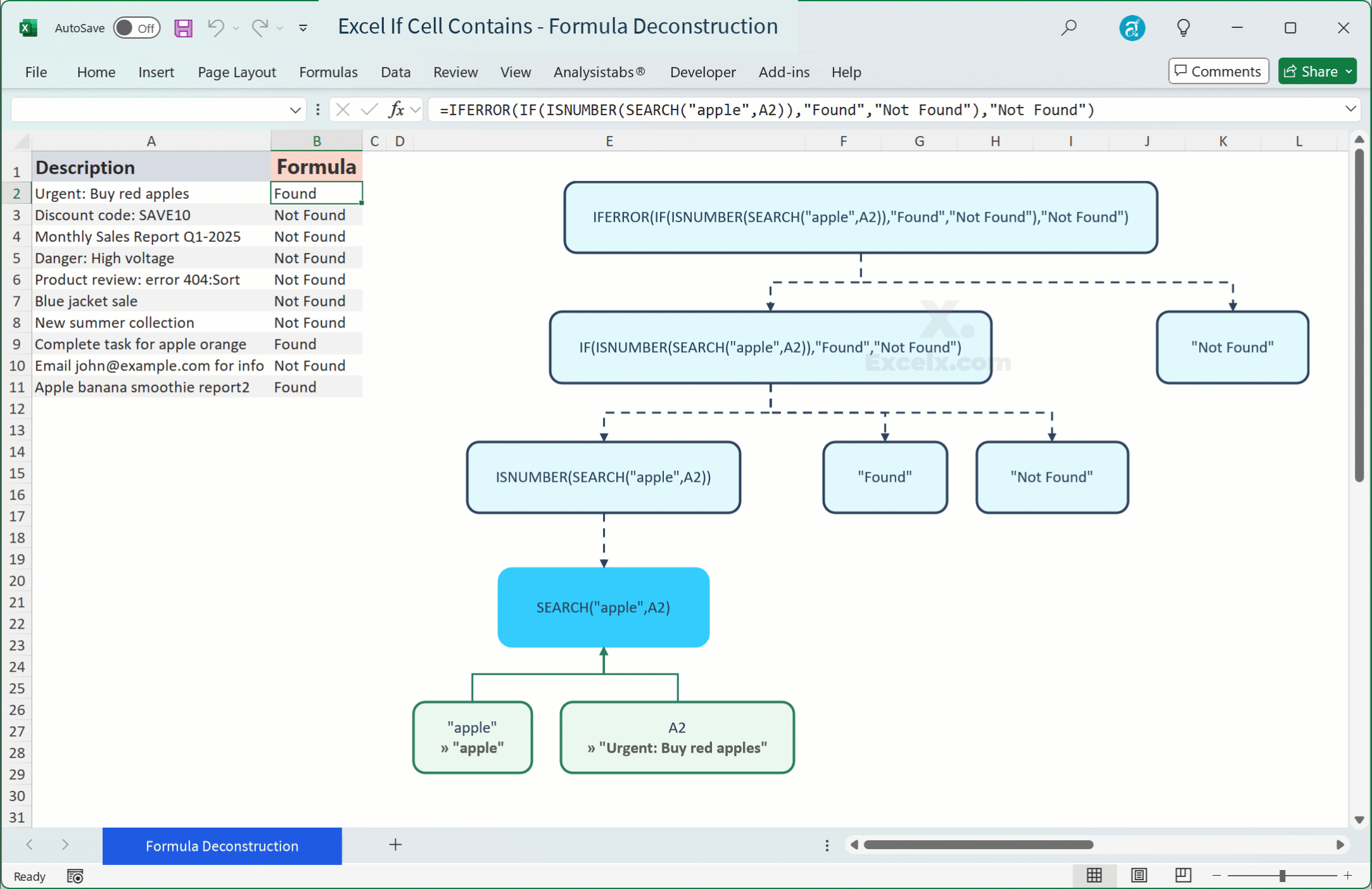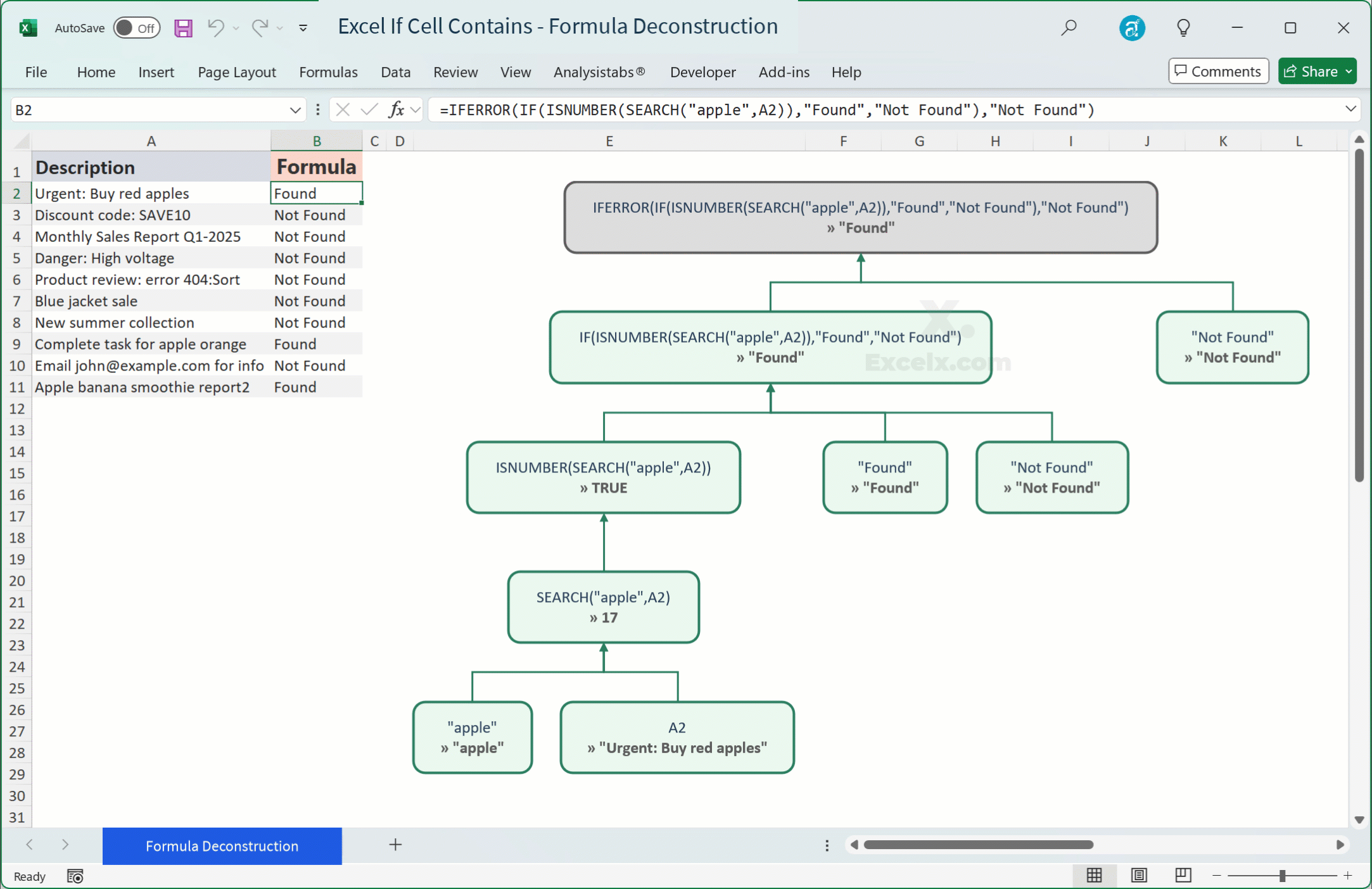
Quick Answer — To check if a cell (e.g., A2) contains specific text (e.g., “apple”), use:
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("apple",A2)),"Found","Not Found")For a case-sensitive check, use
FINDinstead ofSEARCH:=IF(ISNUMBER(FIND("apple",A2)),"Found","Not Found")
Summary: IF Cell Contains Formula Explained
The goal of “IF Cell Contains” in Excel is to evaluate if a cell’s content includes a specific substring or pattern, and then perform an action based on that evaluation. This goes beyond simple exact matches, allowing you to build dynamic and flexible conditional logic in your spreadsheets.
Here’s a common example:
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("urgent",B2)),"High Priority","Normal Priority")This formula checks if cell B2 contains the word “urgent”. If it does, it returns “High Priority”; otherwise, it returns “Normal Priority”.
Real-World Applications: Why “Contains” Matters
Being able to check if a cell contains specific text, rather than an exact match, is incredibly powerful for real-world data analysis and reporting.
- Categorizing Data: Automatically assign categories to products based on keywords in their description (e.g., “organic” or “gluten-free”).
- Flagging Issues: Identify and highlight customer feedback or support tickets that mention specific problems (e.g., “bug”, “error”, “slow”).
- Filtering and Reporting: Extract or sum data where a particular attribute is present within a larger text string, like pulling all sales records for regions containing “North” in their name.
Generic Formula: The Core Logic
At its heart, the “IF Cell Contains” logic relies on combining IF, ISNUMBER, and either SEARCH or FIND.
Here’s the abstract pattern:
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("text_to_find",cell_to_check)), value_if_true, value_if_false)"text_to_find": The specific piece of text you’re looking for within the cell.cell_to_check: The cell containing the text you want to evaluate.value_if_true: What Excel should return iftext_to_findis found.value_if_false: What Excel should return iftext_to_findis not found.
Step-by-Step Explanation: How “IF Contains” Works
Let’s break down the core components of the IF Cell Contains formula:
The SEARCH & FIND Difference
Both SEARCH and FIND functions look for one text string within another. The key difference is case sensitivity:
SEARCH("apple",A2): Case-insensitive. Finds “apple”, “Apple”, “APPLE”, etc.FIND("apple",A2): Case-sensitive. Only finds “apple”.
When SEARCH or FIND finds the text_to_find, it returns the starting position of that text as a number. If the text isn’t found, it returns a #VALUE! error.
Detecting Partial Matches with ISNUMBER
Since SEARCH and FIND return a number (position) or an error, we need a way to convert this into a simple TRUE or FALSE for our IF statement. That’s where ISNUMBER comes in.
ISNUMBER(SEARCH("apple",A2))- If A2 contains “apple” (e.g., “I like apples”),
SEARCHreturns a number (e.g., 8).ISNUMBER(8)evaluates toTRUE. - If A2 does not contain “apple” (e.g., “I like oranges”),
SEARCHreturns#VALUE!.ISNUMBER(#VALUE!)evaluates toFALSE.
- If A2 contains “apple” (e.g., “I like apples”),
Wrapping it in IF
Finally, the IF function takes this TRUE/FALSE result and acts upon it:
=IF(logical_test, value_if_true, value_if_false)
Where logical_test is our ISNUMBER(SEARCH()) or ISNUMBER(FIND()) construction.
For instance, if A2 contains “Red apple”:
SEARCH("apple",A2)returns5.ISNUMBER(5)returnsTRUE.IF(TRUE,"Found","Not Found")returns “Found”.
Animated Walk-through: See It in Action
Watch this quick animation to see how the IF Cell Contains formula comes to life in Excel. 👀
Modern Approach: Streamlining “IF Contains”
While ISNUMBER(SEARCH()) is a classic, modern Excel offers more powerful and often more concise ways to handle “contains” logic, especially when combined with other functions.
XLOOKUP with Wildcards
For looking up values based on partial text, XLOOKUP is a game-changer with its wildcard support:
=XLOOKUP("*"&B2&"*",A:A,C:C,"Not Found",2)This formula looks for any cell in column A that contains the text from B2 and returns the corresponding value from column C. The 2 as the fifth argument enables wildcard character match.
New Text Functions (TEXTSPLIT, TEXTBEFORE, TEXTAFTER)
For extracting specific parts of text based on delimiters or patterns, these new functions are incredibly useful. While not direct “IF Contains” replacements, they can simplify data before you apply conditional logic.
TEXTBEFOREandTEXTAFTER: Extract text before or after a specific delimiter.TEXTSPLIT: Split text into multiple columns based on a delimiter.
Array Formulas with FILTER & UNIQUE
For advanced scenarios where you want to filter or list data based on a “contains” condition, dynamic array functions are superior.
FILTERto show rows that contain specific text:=FILTER(A2:C10,ISNUMBER(SEARCH("urgent",B2:B10)),"No Matches")This formula filters the range
A2:C10to show only rows where columnBcontains “urgent”.UNIQUEto list unique items containing text:=UNIQUE(FILTER(A2:A10,ISNUMBER(SEARCH("blue",B2:B10))))This returns a unique list of items from
A2:A10where the corresponding cell inB2:B10contains “blue”.
Performance Note: Be Mindful of Large Datasets
While powerful, SEARCH/FIND and array formulas can impact performance on very large datasets (tens of thousands of rows or more) if used excessively. For massive-scale text analysis, consider Power Query or VBA. 🚀
Cross-Platform Matrix: Consistency Across Devices
Most IF, SEARCH, FIND, and ISNUMBER functions behave consistently across Excel for Windows, Mac, and Excel for the web. Modern functions like XLOOKUP, FILTER, TEXTSPLIT, TEXTBEFORE, and TEXTAFTER require a Microsoft 365 subscription. Always test your formulas if you’re deploying solutions across different Excel versions or platforms.
Common Pitfalls & Fixes
Even experienced Excel users can stumble on these common issues.
Case Sensitivity Gotcha
- Pitfall: Assuming
SEARCHis always case-sensitive orFINDis always case-insensitive. - Fix: Remember:
SEARCHis case-insensitive (good for general “contains” checks),FINDis case-sensitive (use when capitalization matters). If you needSEARCHto be case-sensitive, you’ll need a more complex array formula or helper column.
Dealing with Errors (#VALUE!, #N/A)
- Pitfall: When
SEARCHorFINDdoesn’t find the text, it returns a#VALUE!error, which can then propagate through yourIFstatement or other calculations. - Fix: Wrap your formula with
IFERROR.=IFERROR(IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("apple",A2)),"Found","Not Found"),"Not Found")Or, a cleaner alternative:
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("apple",A2)),"Found","Not Found")The
ISNUMBERfunction handles the#VALUE!error gracefully by returningFALSE, soIFERRORisn’t strictly necessary for the coreIF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH()))structure, but it’s crucial if you useSEARCHdirectly in other parts of a formula.
Order of Operations
- Pitfall: Misunderstanding how
ANDorORfunctions combine withISNUMBER(SEARCH())for multiple criteria. - Fix: When checking for any of multiple strings, use
OR. When checking for all, useAND. Ensure eachISNUMBER(SEARCH())clause is evaluated independently before combining withOR/AND.
Automation Corner: VBA to Check if Cell Contains
For repetitive “IF Cell Contains” tasks or integrating with larger workflows, VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) or Office Scripts (for web-based automation) can provide powerful solutions. 🤖
VBA Example: Check & Mark Rows
This VBA macro checks column A for “urgent” and marks column B.
Sub CheckForUrgent()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1") ' Change to your sheet name
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp).Row
Dim i As Long
For i = 2 To lastRow ' Assuming data starts from row 2
If InStr(1, ws.Cells(i, "A").Value, "urgent", vbTextCompare) > 0 Then
ws.Cells(i, "B").Value = "High Priority"
Else
ws.Cells(i, "B").Value = "Normal Priority"
End If
Next i
End Sub
InStr is VBA’s equivalent of SEARCH, vbTextCompare makes it case-insensitive.
25 Real-time Examples
Here are 25 practical “IF Cell Contains” examples to supercharge your Excel skills. Assume your data starts in cell A2.
1. IF Cell Contains Specific Text (Basic)
Returns “Yes” if A2 contains “apple”, otherwise “No”.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("apple",A2)),"Yes","No")2. IF Cell Contains Text (Case-Sensitive)
Returns “Yes” if A2 contains “Apple” (exact case), otherwise “No”.
=IF(ISNUMBER(FIND("Apple",A2)),"Yes","No")3. IF Cell Contains Any of Multiple Texts (OR Logic)
Checks if A2 contains “apple” OR “orange” OR “banana”.
=IF(OR(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("apple",A2)),ISNUMBER(SEARCH("orange",A2)),ISNUMBER(SEARCH("banana",A2))),"Fruit Found","No Fruit")4. IF Cell Contains All of Multiple Texts (AND Logic)
Checks if A2 contains “red” AND “apple”.
=IF(AND(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("red",A2)),ISNUMBER(SEARCH("apple",A2))),"Red Apple","Other")5. IF Cell Contains Text and Returns a Value from Another Cell
If A2 contains “product”, return the value from B2.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("product",A2)),B2,"")6. IF Cell Contains Text and Returns a Specific Result
If A2 contains “error”, return “Review”, else “OK”.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("error",A2)),"Review","OK")7. IF Cell Contains Number (as Text)
Checks if A2 contains the digit “5”.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("5",A2)),"Contains 5","Doesn't Contain 5")8. IF Cell Contains a Wildcard Character
Check if A2 contains “report” followed by any single character. Use ? for single character, * for any sequence.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("report?",A2)),"Specific Report","Other")9. IF Cell Does NOT Contain Specific Text
Returns “Safe” if A2 does NOT contain “danger”.
=IF(NOT(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("danger",A2))),"Safe","Danger Detected")10. IF Cell Contains Text, Then Calculate
If A2 contains “discount”, apply a 10% discount to B2.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("discount",A2)),B2*0.9,B2)11. IF Cell Contains Text, Then Conditional Formatting (Rule)
Select range (e.g., A2:A10), then in Conditional Formatting, use “Use a formula to determine which cells to format”.
=ISNUMBER(SEARCH("urgent",A2))12. IF Cell Contains Text and Highlights Entire Row
Select entire range of data (e.g., A2:Z10), then in Conditional Formatting, use “Use a formula…”.
=ISNUMBER(SEARCH("urgent",$A2))(Note the $ before A to lock the column).
13. IF Cell Contains Text in a List (Modern XMATCH)
Check if A2 contains any text from a list in D2:D5.
=IF(OR(ISNUMBER(SEARCH(D2:D5,A2))),"Match Found","No Match")(This is an array formula, might require Ctrl+Shift+Enter in older Excel versions.)
14. Counting Cells That Contain Specific Text
Counts how many cells in A2:A10 contain “report”.
=SUMPRODUCT(--ISNUMBER(SEARCH("report",A2:A10)))15. Summing Values Based on “Contains” Criteria
Sums values in B2:B10 if corresponding cell in A2:A10 contains “sales”.
=SUMIF(A2:A10,"*sales*",B2:B10)(Note: SUMIF and COUNTIF natively support wildcards! 😉)
16. Average Based on “Contains” Criteria
Averages values in B2:B10 if corresponding cell in A2:A10 contains “Q1”.
=AVERAGEIF(A2:A10,"*Q1*",B2:B10)17. Extracting Text After Specific String
If A2 contains “ID:”, extract everything after it.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("ID:",A2)),TRIM(MID(A2,SEARCH("ID:",A2)+LEN("ID:"),255)),"")Modern Excel: =TEXTAFTER(A2,"ID:")
18. Extracting Text Before Specific String
If A2 contains ” – “, extract everything before it.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH(" - ",A2)),LEFT(A2,SEARCH(" - ",A2)-1),"")Modern Excel: =TEXTBEFORE(A2," - ")
19. If Cell Contains Either X Or Y, But Not Both
A more complex scenario, often handled with nested IFs or XOR.
=IF(XOR(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("apple",A2)),ISNUMBER(SEARCH("orange",A2))),"Either but not both","Mixed")20. IF Cell Contains, Then VLOOKUP
If A2 contains “code”, then lookup value in B2 using VLOOKUP.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("code",A2)),VLOOKUP(B2,D:E,2,FALSE),"")21. IF Cell Contains and Concatenate
If A2 contains “new”, add “(New!)” to the end of C2.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("new",A2)),C2&" (New!)",C2)22. Checking for Presence of Any Text (Not Blank)
If A2 contains any text (not just blank).
=IF(A2<>"","Contains Text","Is Blank")(This is a general check, not “contains” a specific substring)
23. IF Cell Contains a Specific Character (e.g., “@”)
Checks for the “@” symbol, useful for email addresses.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("@",A2)),"Valid Email Format?","Not Email")24. IF Cell Contains Text, Return 1, Else 0 (for counting)
A simple way to create a binary flag.
=--(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("complete",A2)))(The -- converts TRUE/FALSE to 1/0)
25. IF Cell Contains Text, Then Combine with INDEX/MATCH
If A2 contains “lookup”, perform an INDEX/MATCH operation on B2.
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("lookup",A2)),INDEX(D:D,MATCH(B2,C:C,0)),"")Accessibility Tip: Make Your Formulas Readable
For complex IF statements, use line breaks (Alt + Enter within the formula bar) to break up clauses. This significantly improves readability, especially for others who might need to understand or debug your work. Add comments (using N("Your comment here")) for extra clarity within formulas, although this is more common in VBA.
Download the Practice File
Ready to try these examples yourself? Download the Excel IF Cell Contains Practice File and follow along! 💾
FAQ
How do I use IF Cell Contains in Excel?
To use IF Cell Contains, you typically combine the IF function with ISNUMBER and SEARCH (for case-insensitive) or FIND (for case-sensitive). The basic formula is =IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("text",Cell)),"True Result","False Result"). This checks if “text” is found in “Cell”.
What is the formula for IF Cell Contains in Excel?
The most common formula for IF Cell Contains (case-insensitive) is:
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("your_text",A1)),"Found","Not Found")For case-sensitive matching, replace SEARCH with FIND.
How do I check if a cell contains specific text in Excel?
You can check if a cell contains specific text by embedding the SEARCH or FIND function within an ISNUMBER function, and then using that as the logical test for an IF statement. For example: =ISNUMBER(SEARCH("keyword",B5)) will return TRUE if ‘keyword’ is found in cell B5, otherwise FALSE.
Can I use wildcards with IF statements in Excel?
Yes, SEARCH naturally supports wildcards (* for any sequence of characters, ? for any single character). This means your IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH())) formulas can use wildcards directly. Functions like COUNTIF, SUMIF, and XLOOKUP also support wildcards.
How to use IF with SEARCH in Excel?
IF with SEARCH is the primary method for case-insensitive ‘contains’ checks. SEARCH returns the starting position number if the text is found, or an error if not. ISNUMBER converts this to TRUE/FALSE, which IF then uses. Example: =IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("report",C2)),"Match","No Match").
How do I make IF cell contains case-insensitive?
To make IF Cell Contains case-insensitive, always use the SEARCH function instead of FIND. SEARCH inherently performs a case-insensitive lookup, while FIND is case-sensitive.
Glossary
SEARCHfunction: An Excel text function that finds one text string within another, returning the starting position of the first string. It is case-insensitive and supports wildcards.FINDfunction: Similar toSEARCH, but it is case-sensitive and does not support wildcards.ISNUMBERfunction: Checks if a value is a number, returningTRUEorFALSE. Used to convert the output ofSEARCH/FIND(number or error) into a boolean.- Wildcard Characters: Special characters used in search operations:
*(asterisk) matches any sequence of characters, and?(question mark) matches any single character. - Dynamic Arrays: A feature in modern Excel that allows a single formula to spill results into multiple cells. Functions like
FILTER,UNIQUE,SORT, etc., are dynamic array functions.
Related Formulas
COUNTIF(range,"*text*"): Counts cells in a range that contain specific text.=COUNTIF(A:A,"*apple*")SUMIF(range,"*text*",sum_range): Sums values in a range based on a “contains” criterion.=SUMIF(A:A,"*Q1*",B:B)IFERROR(value, value_if_error): Handles errors gracefully, returning a specified value if the first argument results in an error.=IFERROR(VLOOKUP(A2,B:C,2,FALSE),"Not Found")
Related Functions
LEFT,RIGHT,MID: Extract parts of a text string from the beginning, end, or middle.LEN: Returns the number of characters in a text string.TRIM: Removes extra spaces from text.CONCATENATE(&): Joins several text strings into one.FILTER,UNIQUE: Modern dynamic array functions for filtering and extracting unique lists based on criteria.
Next-Step Learning Path
Ready to dive deeper? Explore these related topics to further enhance your Excel skills: 🎓
- Mastering Wildcards: Understand the full power of
*,?, and~in Excel formulas. - Advanced
IFStatements: Learn about nestedIFs,IFSfunction, and combiningIFwithAND/OR. - Introduction to Array Formulas: Unlock more complex data manipulation with functions that operate on ranges.
- Power Query for Text Transformation: For very large datasets or complex text cleaning, Power Query is your next step.